Principles

Automatic Potentiometric Titrator
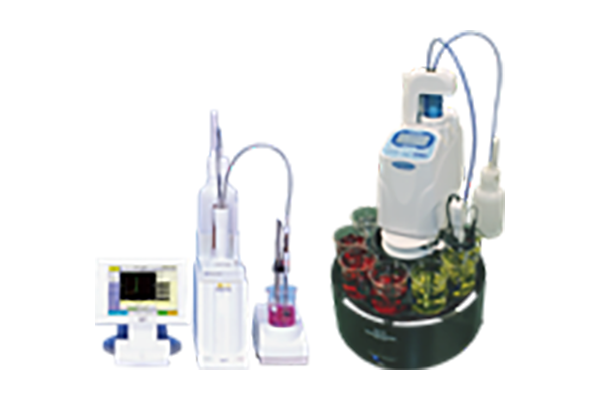

What is a Titrator

A titrator uses the analysis method wherein the sample is made to react with a reagent solution whose concentration is known, and from the volume of the reacted reagent, the result is determned.
Previously, this was judged by the change in indicator solution color when the reagent was dispensed from a glass burette.
Now, the “Automatic Potentiometric Titrator” automatically dispensed reagent, determines endpoint, and calculates concentration!
Measurement Principles of KEM Automatic Potentiometric Titrator
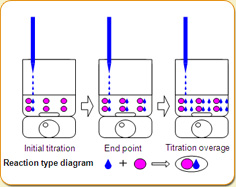
Using the constant reaction between the substance to be measured in the sample and a substance of known concentration, by measuring the amount of consumption of the reagent when it is dispensed in, it can be ascertained how much of the substance to be measured is contained in the sample.
In hand analysis, the indicator solution is used to detect the endpoint by color change.With a titrator, the potentiometry (pH) change from electrical polarization is used to find the endpoint.
Where is a Titrator used?
Industrial Chemicals
[quality control/inspection/testing/research]
Food/Food Processing
[quality control/analysis/testing]
Fats
[inspection/manufacture/development]
Petroleum Products
[quality control/inspection/testing]
Pharmaceuticals/Drugs/Cosmetics
[quality control/development]
Drinking Water
[analysis/testing]
Plating Industry
[inspection/manufacture/development]
Titrator are used in all manner of industries for quality control, inspection, and testing-related divisions.
Please link to the application here.
Automatic Potentiometric Titrator / Karl Fischer Moisture Titrator
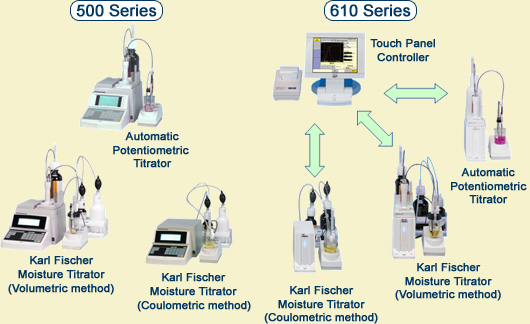
What are the advantages of using a Titrator?
Improved measurement data reliability
Data reliability is improved because the device uses high-precision electric burettes and sensors.
No difference due to human error
With analysis by hand, it is a matter of course that different measurements occur with the same sample, but when the task is left to the device, the same value results, no matter who is doing the measuring.
Automation becomes possible
With the use of such options as a multiple sample changer, the device can measure several samples on its own, after the samples have simply been lined up.
Measurement can be performed without experience or specialized skills
In analysis, there are cases in which one must have mastery of skills or years of experience. However, if one simply learns how to use the device, every person can analyze at the same level.
What kinds of analysis are performed? [titrator]
Industrial chemical analysis
| Item for analysis | Analysis method | Applicable standard |
|---|---|---|
| Salicylic acid purity | acid-base titrator | JIS K8392 |
| Boric acid purity | acid-base titrator | JIS K8363/ISO 6353-3 |
| Benzoic acid purity | acid-base titrator | JIS K8073 |
| Hydrochloric acid | acid-base titrator | JIS K8180/ISO 6353-2 |
| Formic acid | acid-base titrator | JIS K8264 |
| Nitric acid | acid-base titrator | JIS K8541/ISO 6353-2 |
| Acetic acid | acid-base titrator | JIS K8355/ISO 6353-2 |
| Sodium hydroxide solution | acid-base titrator | JIS K8625/ISO 6353-2 |
| Sodium carbonate solution | acid-base titrator | JIS K8625/ISO 6353-2 |
| Sulfuric acid | acid-base titrator | JIS K8951/ISO 6353-2 |
| Iodine solution | oxidation-reduction titrator | JIS K8920/ISO 6353-2 |
| Iron chloride (III) hexahydrate purity | oxidation-reduction titrator | JIS K8142 |
| Sodium hypochlorite solution concentration | oxidation-reduction titrator | JIS K8001 |
| Magnesium chloride purity | chelatometric titration | JIS K8159/ISO 6353-2 |
| Sodium carbonate acid disassociation constant | acid-base titrator |
Food analysis
| Item for analysis | Analysis method | Applicable standard |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement of orange juice acidity | acid-base titrator | fruit drinks JAS/ISO 750 |
| Measurement of grape juice acidity | acid-base titrator | fruit drinks JAS/ISO 750 |
| Measurement of apple juice acidity | acid-base titrator | fruit drinks JAS/ISO 750 |
| Measurement of lemon juice concentrate acidity | acid-base titrator | fruit drinks JAS/ISO 750 |
| Measurement of worcester sauce acidity | acid-base titrator | worcester sauce JAS |
| Measurement of apple vinegar acidity | acid-base titrator | vinegar AS |
| Measurement of worcester sauce salt content | precipitation titrator | worcester sauce JJAS |
| Measurement of soy sauce salt content | precipitation titrator | soy sauce JAS |
| Vitamin C in lemon tea | oxidation-reduction titrator | fruit drinks JAS |
| Vitamin C in soft drinks | oxidation-reduction titrator | fruit drinks JAS |
| Measurement of red wine acidity | acid-base titrator | National Tax Agency- prescribed analysis method |
| Measurement of white wine acidity | acid-base titrator | National Tax Agency- prescribed analysis method |
| Total acid of alcohol (free acid) | acid-base titrator | National Tax Agency- prescribed analysis method |
| Amino acid in Japanese Sake | acid-base titrator | National Tax Agency- prescribed analysis method |
Fat analysis
| Item for analysis | Analysis method | Applicable standard |
|---|---|---|
| Fat saponification | acid-base titrator (anhydrous) | JIS K0070/ASTM D5558/fat standard analysis method (I) |
| Oleic acidity | acid-base titrator (anhydrous) | JIS K0070 |
| Oleic acid iodization | oxidation-reduction titrator | Fat standard analysis method (II)/ISO 3960 |
| Oleic acid overoxidization | oxidation-reduction titrator | JIS K0070/ASTM D1959/ISO 3961 |
Petroleum Products analysis
| Item for analysis | Analysis method | Applicable standard |
|---|---|---|
| Grease basicity measurement | acid-base titrator (anhydrous) | JIS K2501/ASTM D2896/ISO 3771 |
| Grease acidity measurement | acid-base titrator (anhydrous) | JIS K2501/ASTM D664/ISO 6619 |
| Cyclohexene bromine value measurement | polarization titrator | JIS K2605/ISO 3839 |
Pharmaceuticals/Drugs analysis
| Item for analysis | Analysis method | Applicable standard |
|---|---|---|
| Gastrointestinal medicine sodium acid carbonate | acid-base titrator | Japan Pharmacopoeia 14 |
| Antibiotic benzalkonium chloride | oxidation-reduction titrator | Japan Pharmacopoeia 14 |
| Indenoral hydrochloride | acid-base titrator | Japan Pharmacopoeia 14 |
| Chlorpropamide | acid-base titrator | Japan Pharmacopoeia 14 |
| Salicylic acid | acid-base titrator | Japan Pharmacopoeia 14 |
Drinking water testing
| Item for analysis | Analysis method | Applicable standard |
|---|---|---|
| Drinking water hardness measurement | chelate titrator | JIS K0102/ASTM D1126/ISO 6059 |
| Drinking water calcium hardness measurement | chelate titrator | JIS K0101/ASTM D1126/ISO 6058 |
| Drinking water magnesium hardness measurement | chelate titrator | JIS K0101 |
Plating fluid analysis
| Item for analysis | Analysis method | Applicable standard |
|---|---|---|
| Plating fluid chrome oxide (anhydrous chrome acid) | oxidation-reduction titrator | |
| Nickel (plating) liquid nickel chloride | precipitate titrator | |
| Silver plating fluid silver precipitate titrator | precipitate titrator | |
| Zinc plating NaCN | precipitate titrator | |
| Copper plating fluid Cu, CuCN | chelate titrator | |
| Solder plating fluid tin | oxidation-reduction titrator |
What is a Neutralization Titration?
[Neutralization Titration]
Among representative substances called acids, there are such acids as hydrochloric acid, nitric acid, and sulfuric acid.
These acids, besides both changing blue-colored litmus to red, share the properties of reacting to such metals as magnesium and producing oxygen thereby.
Acid electrolytically disassociates as follows, and produces hydrogen ions (H+).
For example, hydrochloric acid electrolitically disassociates this way:
HCl → H+ + Cl-
Also, alkali is a substance which, in addition to changing red-colored litmus to blue, reacts with acid to cause it to lose its acid qualities.
The representative substances called alkali include sodium hydrate, potassium hydrate, and calcium hydrate.
Alkali electrolitically disassociates as follows, and produces hydroxide ions (OH-).
For example, sodium hydrate electrolitically disassociates this way:
NaOH → Na+ + OH-
When a sodium hydrate (NaOH) solution is gradually added to hydrochloric acid (HCI), the acidic qualities of the acid slowly weaken, and eventually both the acidic and alkaline qualities are lost. When this state is achieved, it is said to have reached the point of neutralization.
[Hydrochloric Acid]
HCl ⇔ H+ + Cl-
H+ + OH- → H2O
[Sodium Hydrate]
NaOH ⇔ Na+ + OH-
Looking at hydrogen ion concentration and number of hydroxide ions which have reached the point of neutralization, the amount of hydrogen ions emitted from the acid, and the amount of hydroxide ions emitted from the alkali, have become equal.
The reaction between acid and alkali is called a neutralization reaction, and the method of using this reaction to find the amount of alkali or acid for which the concentration is not known is called neutralization titration.